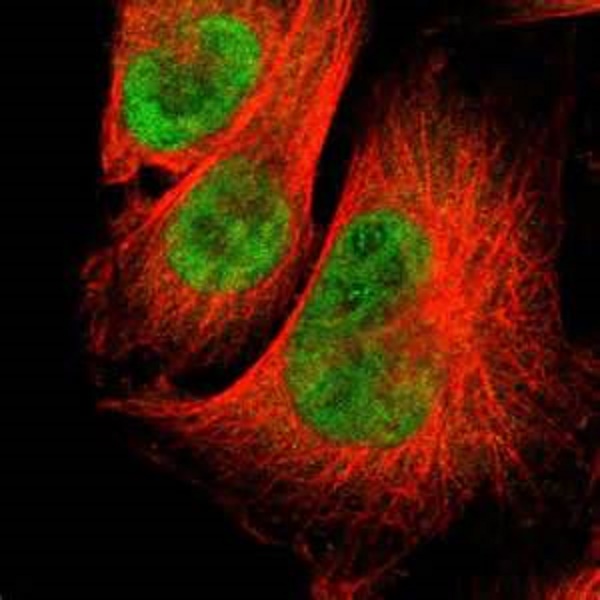
Cells also communicate with each other. Cell publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology, molecular biology, neuroscience, immunology, virology and microbiology, cancer, human genetics, systems biology, signaling, and disease mechanisms and therapeutics. Eukaryotic cells, which possess a nucleus, and prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. All cells are capable of replication, protein synthesis, and motility. Most cells have one or more nuclei and other organelles that carry out a variety of tasks. Usually microscopic in size, cells are the smallest structural units of living matter and compose all living things. · cells are the basic units of life. · a cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism, typically microscopic, consisting of cytoplasm and a membrane, and in most cases containing a nucleus and organelles. · a cell is a mass of cytoplasm that is bound externally by a cell membrane. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: The body contains around 50—100 trillion cells, and they vary widely in size, number, structure, and use.
Cell Types Their Secret Weapon The Effector Response
Cells also communicate with each other. Cell publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology,...