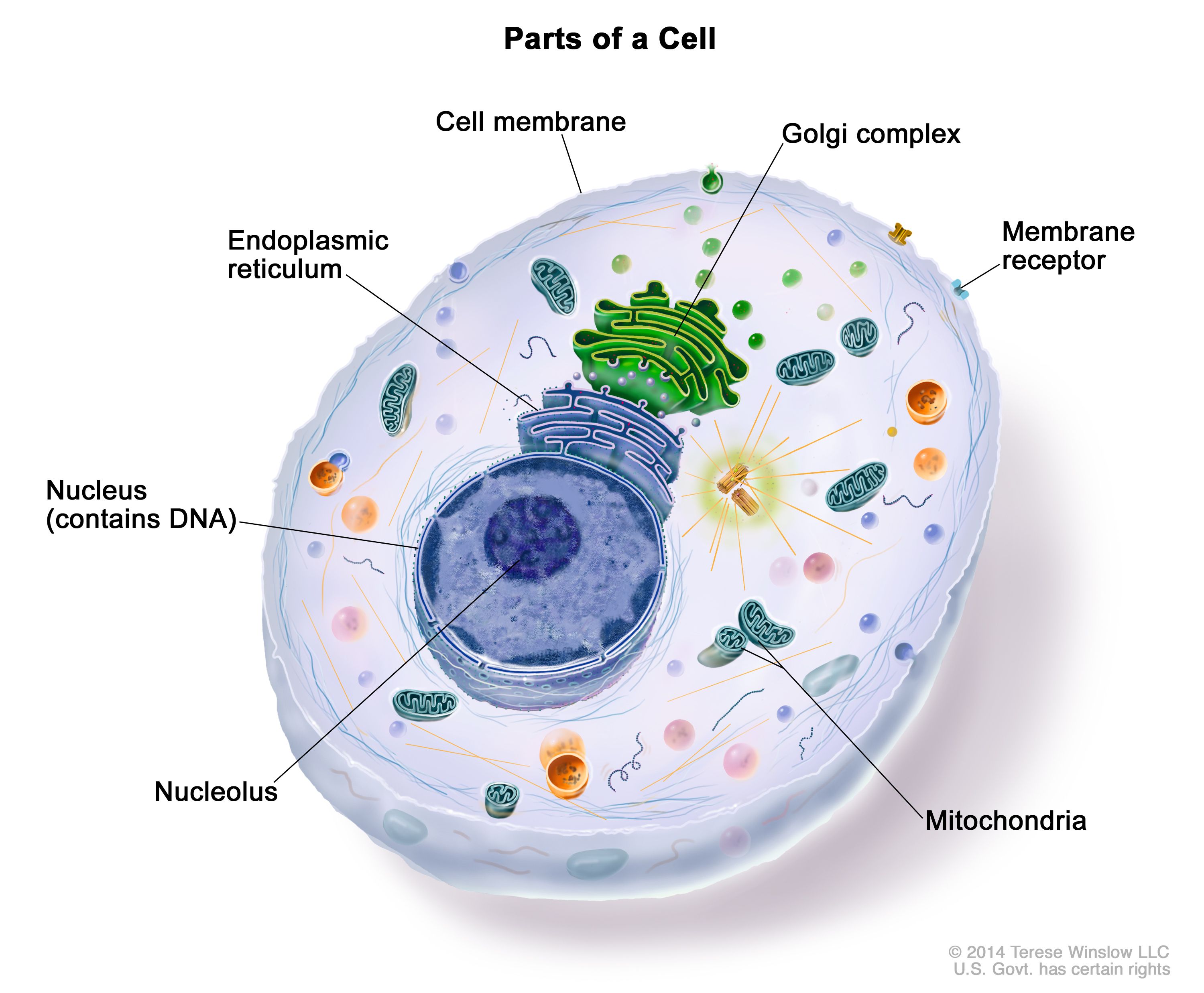
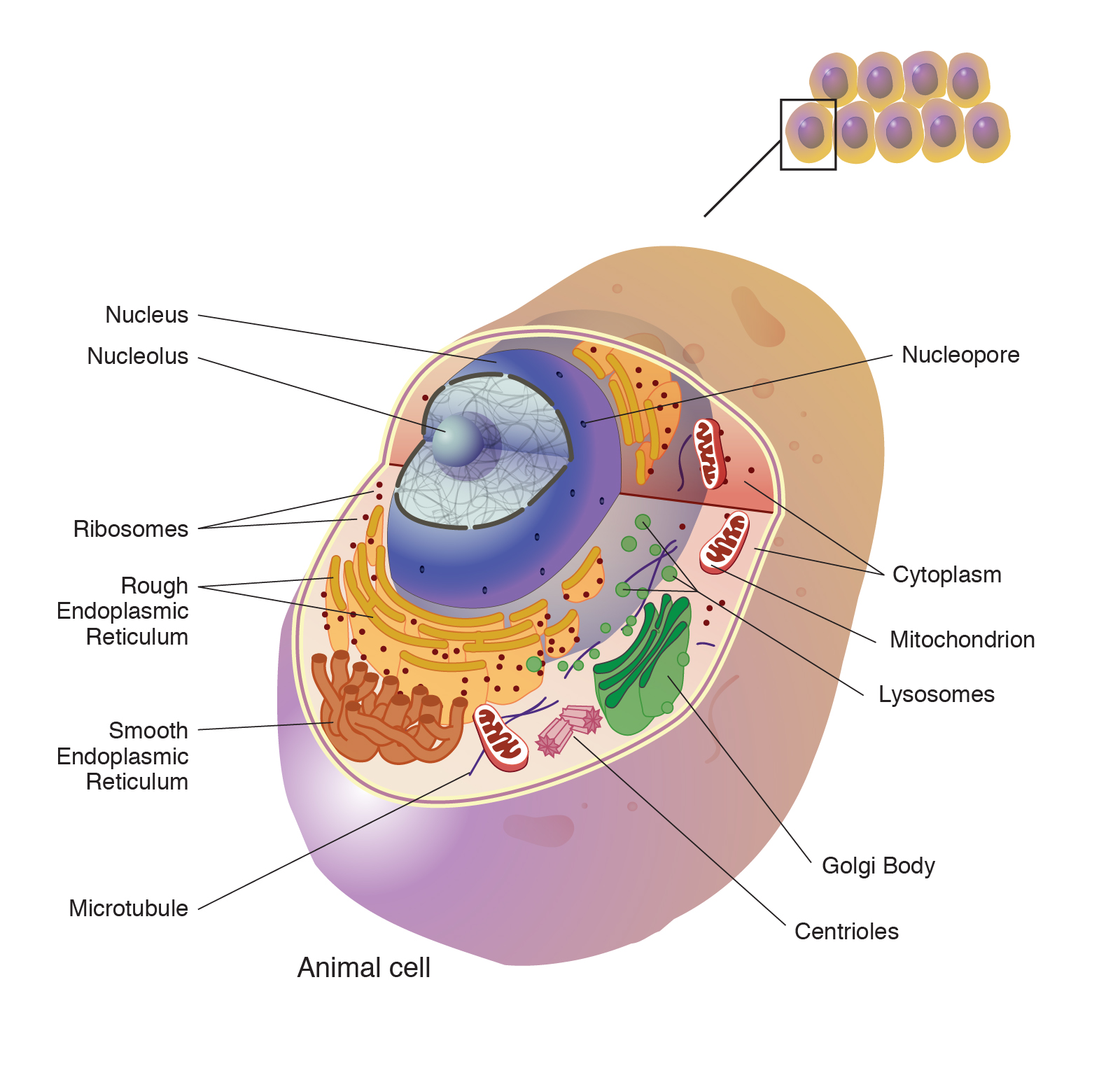
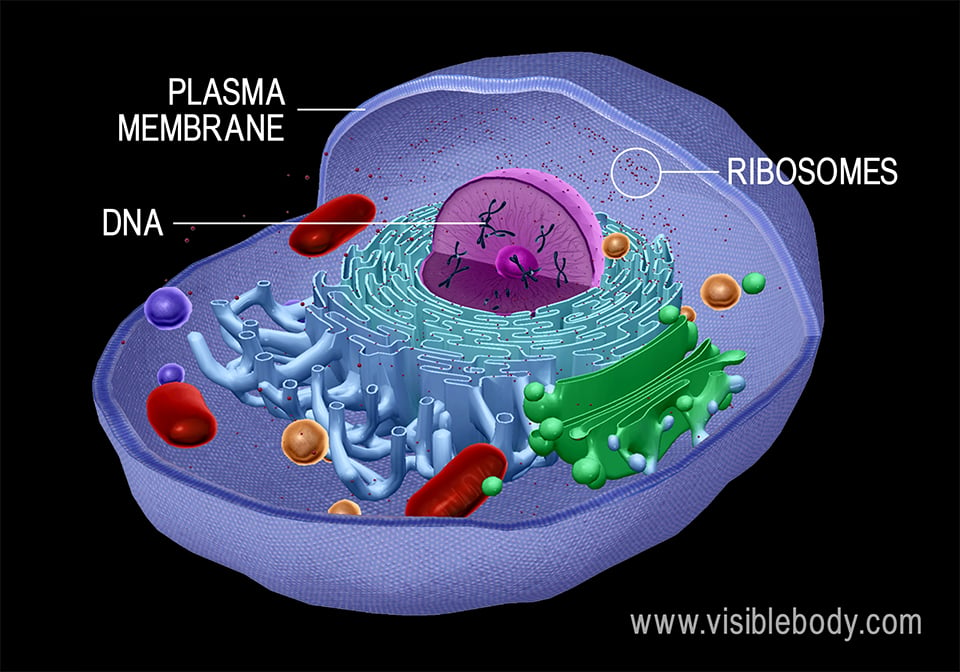
· human cells contain the following major parts, listed in alphabetical order: Cell publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology, molecular biology, neuroscience, immunology, virology and … Cells are broadly categorized into two types: All cells are capable of replication, protein synthesis, and motility. Within cells, the cytoplasm is made up of a jelly-like fluid (called the cytosol) and other structures that … · a cell is a mass of cytoplasm that is bound externally by a cell membrane. · cells are the basic units of life. · a cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of an organism, typically microscopic, consisting of cytoplasm and a membrane, and in most cases containing a … All cells evolved from a common ancestor and use the same kinds of carbon-based molecules. Cells also communicate with each … Usually microscopic in size, cells are the smallest structural units of living matter and compose all … Eukaryotic cells, which … Learn how cell function depends on a diverse group of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and sugars. The body contains around 50—100 trillion cells, and they vary widely in size, number, structure, and use.
Cell Wall Diagram Made Easy Learn In Minutes
· human cells contain the following major parts, listed in alphabetical order: Cell publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including...