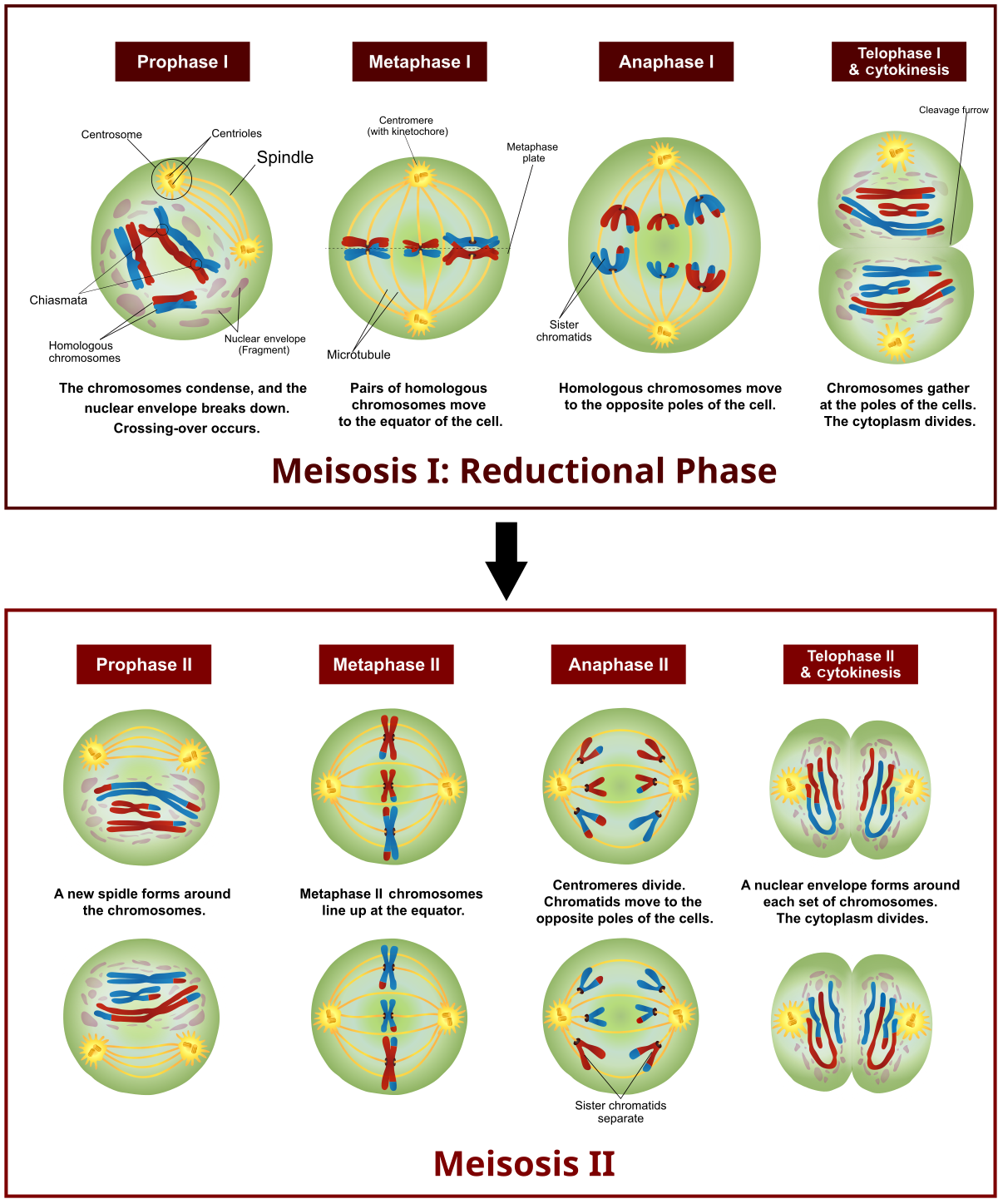
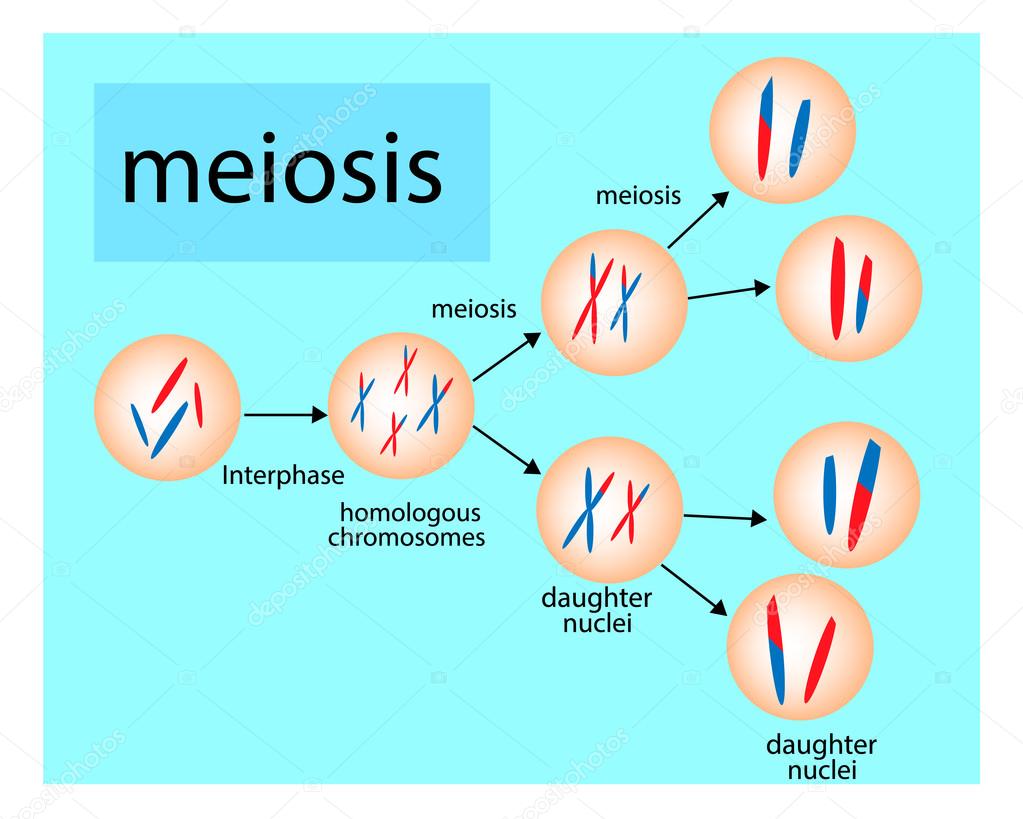
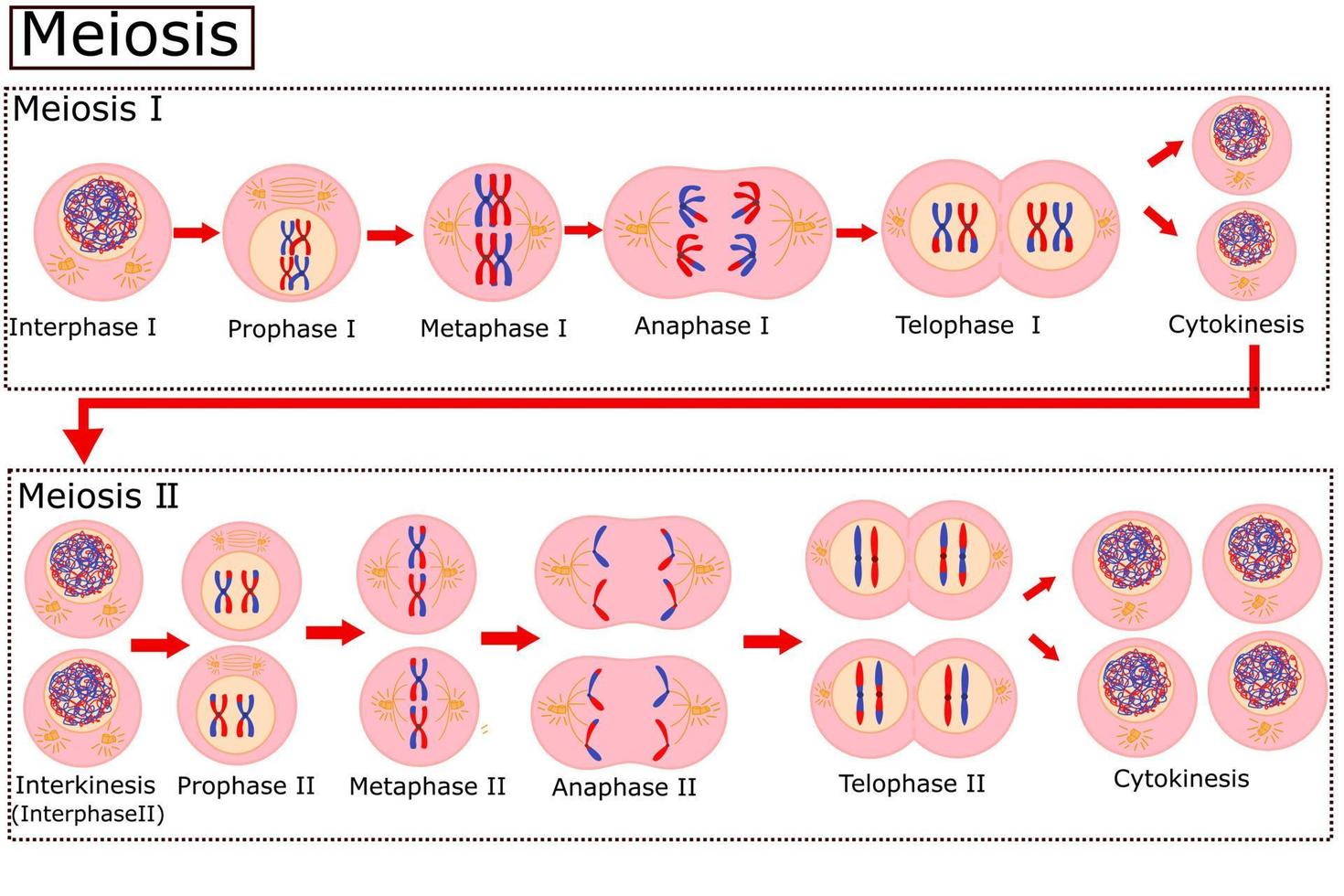
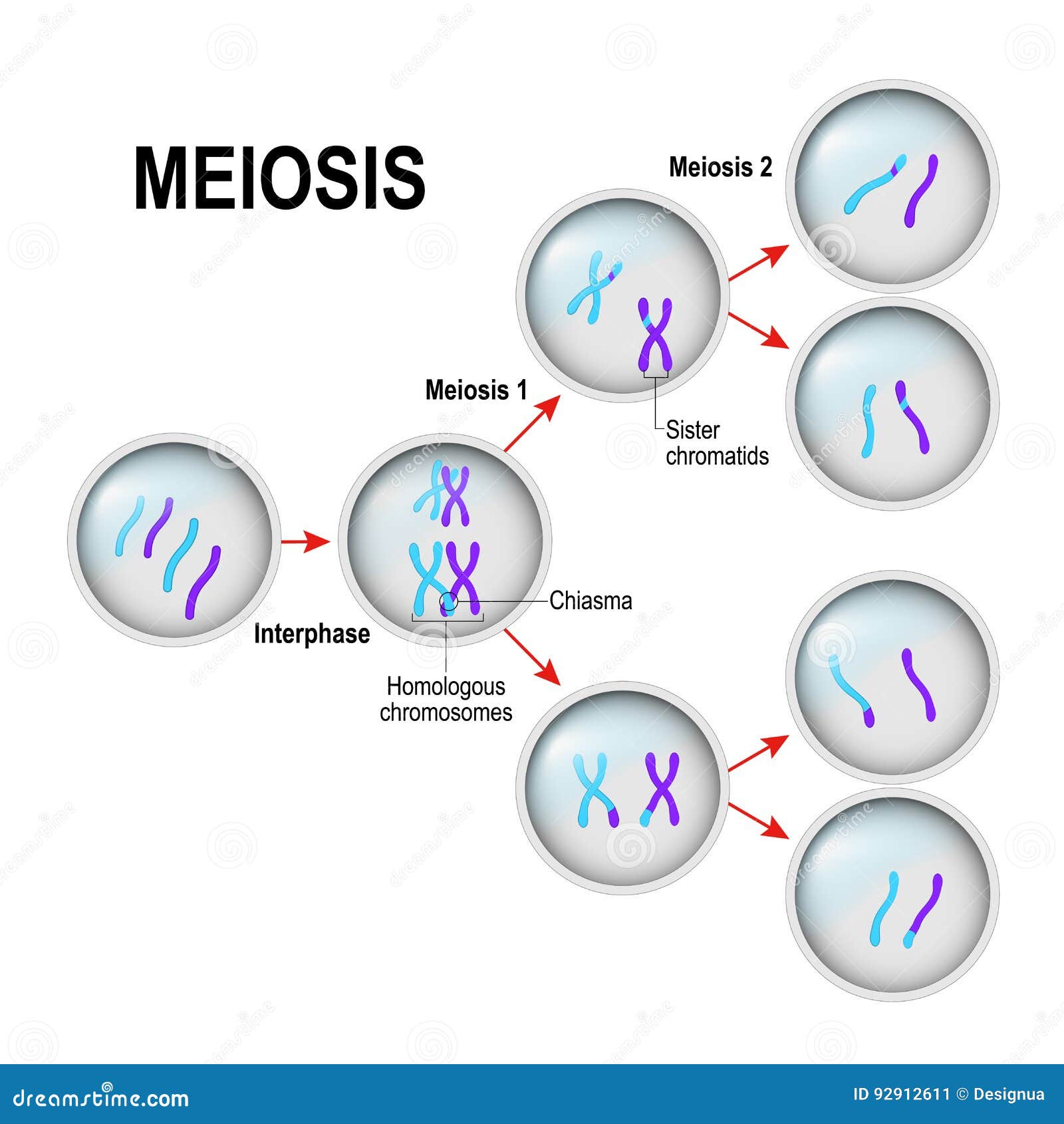
· meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half (2n to n), leading to the formation of four non-identical daughter cells. And egg cells in plants. These are gametes, so sperm or eggs (ova). Most siblings have different appearances because they each receive a unique combination of genes from their parents. As a cell divides to form gametes: These are sperm and eggs (ova) in animals, and pollen and ova in. Meiosis (/ maɪˈoʊsɪs / ⓘ) [a] is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. · meiosis is the process in eukaryotic, sexually-reproducing animals that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell before reproduction. Many organisms package these cells into … · meiosis is a type of cell division in sexually reproducing eukaryotes, resulting in four daughter cells (gametes), each of which has half the number of chromosomes as compared to … It’s the architect behind the genetic uniqueness of siblings, the reason for the variation in eye color, the engine of evolution, and the key to fertility. This short video explains the role of meiotic cell division. The process of meiosis produces four daughter cells that are genetically non-identical. Meiosis produces four non-identical haploid gametes (sex cells). It involves two rounds of division … · meiosis is not just a mechanism. It is crucial for sexual … Sexual reproduction uses the process of meiosis , which creates gametes. This is due to a process called meiosis, where the chromosomes from each … The process of meiosis happens in the male and female reproductive organs. · meiosis is a cell division process where a single (parent) cell divides twice to produce four independent (daughter) cells, each having half the chromosomes as the original cell. Listen to the full series on bbc. · meiosis, division of a germ cell involving two fissions of the nucleus and giving rise to four gametes, or sex cells, each with half the number of chromosomes of the original cell.
Meiosis Why You Look Like Your Parents But Not Exactly
· meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half (2n to n), leading to the formation of four non-identical...